Geometric's CAMWorks® infuses a sense of urgency with 'quicker is better' at …
This enhanced ability to leverage feature-based machining for complex requirements in combination with Intelligent Knowledge Base (TechDB™) allows end users to eliminate the routine elements in CNC programming and focus on their core expertise …
Read more on MCADCafe (press release)
China

Cool China China Machining Parts images
A few nice china China machining parts images I found:
Chinese Rock, Paper, Scissor

Image by Wootang01
15.5.09
We’re driving towards the orphanage. The highway is lonely, save for a few languid trucks ambling along. It is damp too, and a thick fog covers the countryside: a single light here or there provides the only hint of civilization amidst the interminable verdure. Inside the van, the smoke of cigarettes past wafts in the air, lingering like a lost soul. I inhale, and quickly cough. I subsequently open the window to the enveloping darkness outside, so slightly as to not disturb my companions in the back. The roar of the road echoes in my ears.
An unexpected wrench was thrown into our travel plans today. The trip began expediently enough as the bus on which Candy and I rode reached the Shenzhen airport with hours to spare; however, the unscheduled hiccups soon followed. We received an announcement over the public address system notifying us of a flight delay, due to a mysterious military maneuver, we deduced, high in the Shenzhen skies. Several more sonorous reminders came in punctual succession over the next six hours. It seemed as though we would be stuck, stranded really, at the airport forever, or for the day at least. Thankfully, after the police arrested some of the more aggrieved passengers, we finally boarded the plane and took off for central China. We were blessed to be on our way at last, none of us having blown a gasket during the afternoon tedium.
One more pitch black road awaited, down a single lonely lane lined with swarthy trees, standing as though sentries, and at length we arrived at the orphanage. The car stopped in a clearing, and we stepped out, onto a cement lot with soft puddles spread silently beneath our feet. We squinted into the twilight, our eyes trying to make sense of the surroundings. Our bags were unloaded, we made our way to the rooms, and soon enough fell asleep. I think we all enjoyed the repose, rendered especially comfortable by the new guest rooms in which we were staying.
16.5.09
We have only been here for barely 24 hours, yet it feels as though we have been here for much longer, as if time at some point in our journey decided to slow itself to a crawl. Maybe it was because of the litany of activities that we packed into the span of several hours, or perhaps it was the lack of worldly distractions, allowing us to focus solely on our mission, that caused us to suspend the hands of that imaginary clock in our mind. Whatever the case, we’ve enjoyed every minute at the orphanage; it is time definitely well spent in service!
Morning call was at 6:20; and after a prayer meeting we went down to finally visit the kids. They were playing on the vast driveway of the orphanage, savoring their moment of freedom before breakfast. To see so many friendly faces, in spite of their precarious physical and filial circumstance was definitely encouraging. I made a multitude of new friends; and did my best throughout the day to impact those kids with joy, honesty and patience. It is a powerful cocktail which brings love immediately to many.
The food at the orphanage is without processing, as natural as victuals can be in these days of impersonal industrial production. Large chunks of mantou, steaming bowls of soupy congee, and salty vegetables with slivers of meat have characterized our meals. It is the kind of humble stuff that lengthens life spans, and disciplines the palate.
We presented a wide range of activities – structured and unstructured; whole class and small group – to the kids, in the hope that we would manage them as much as amuse. In the morning, as though breaking the ice once were not enough, we ran through a series of dizzying, if not at times totally incoherent, activities designed to familiarize our dispositions to each other. Later, we established a makeshift fun fair, at which we ushered the children to rooms filled with (board) games, and puzzles, and other, more colorful activities such as face painting and balloon making. The kids couldn’t at length contain their enthusiasm, busting into and out of rooms with impunity, soaking in the rapturous atmosphere. In the afternoon, our team attempted to tire them out: running topped the agenda, and by leaps and bounds, the activities, whether straightforward relays or schoolyard classics like duck duck goose and red light, green light, indeed began to tucker our charges out. We, too, were pretty beat by the time night began to creep over the horizon!
17.5.09
Yesterday evening, we surprised the students with a musical performance, followed by forty minutes of bubble-blowing madness; to be sure, the students could not appreciate our somewhat accurate rendition of Amazing Grace so much as the innocent madness of dipping one’s hands in a solution of dish detergent and corn syrup and then whispering a bubble to life; and indeed, the moment the Disney branded bubble-making machines churned the first batch of bubbles into the air, with much rapidity weaving their frenetic pattern of fun, chaos erupted in the room. The students stormed the soap basin, and almost overwhelmed my teammates who valiantly held the Snitch and Pooh high above the heads of the clamoring kids.
During the evening’s festivities, I grew progressively ill, until at last I dashed out of the room to sneeze. Outside, in the cool of the night, under a cloud of stars beaming so far away in the deep of space, I exploded in a rancor of sneezing. The fit lasted for five minutes, an inexorable depression in my system which sent both my body and my esteem tumbling down. I felt bad, not only for my exceedingly rickety health, but for my teammates and the children who may have been exposed to my sickness as it incubated within me; furthermore, everyone in the classroom was saying goodbye and all I could do was rid myself of a sniffle here and there, in between rounds of bursting from nostrils and sinuses. I was impotent, as though one of my insignificant droplets on the floor!
18.5.09
We are in a car heading towards a famous historical site in Henan. The driver’s drawl slips slowly from his mouth, and what he says resonates intelligibly in our ears. Candy, Tanya and the driver are discussing Chinese mythology, and history, which, for better or for worse seem to be inextricably intertwined. We narrowly just now missed hitting an idle biker in the middle of the road; in dodging our human obstacle, the car swerved into the oncoming traffic, sending us flying inside the cabin. Reciting a verse from a worship song calmed our frazzled nerves.
How to describe the children? Many of them smiled freely, and were so polite when greeted that undoubtedly they had been trained well at some point in the tumult of their life education. Precociousness was also a common characteristic shared by the kids, whose stunted bodies belied the mature, perspicacious thoughts hiding just underneath the skin. Of course, in our time together we were more merry than serious, that quality being best left for the adults working silently in their rooms; and to that effect, the kids brought out their funny bones and jangled them in the air to stir up the excitement and to destroy by a jocular clamor any hint of a dull moment – we really laughed a lot. At last, although not all of them seemed interested in our staged activities – rather than feign enthusiasm and eagerness, some skipped our events altogether – those who did participate, most of them in fact, enjoyed themselves with abandon, helping to create that delightful atmosphere where the many sounds of elation reign.
Of the students whom I had the opportunity to know personally, several still stick out in my mind, not the least for my having christened a few of them with English names! David was bold, and courageous, willing to soothe crying babes as much as reprimand them when their capricious actions led them astray; he had a caring heart not unlike a shepherd who tends to his young charges. Edward, who at 13 was the same age as David, definitely grew emotionally, not to mention physically attached to me. He was by my side for much of the weekend, grabbing onto my hand and not letting go, to the point where I in my arrogance would detach my fingers within his, ever so slightly, as if to suggest that a second more would lead to a clean break – I know now that with the cruel hands of time motoring away during the mission, I shouldn’t have lapsed into such an independent, selfish state; he should have been my son. Another child who became so attached to the team as to intimate annoyance was the boy we deemed John’s son, because the boy, it seemed, had handcuffed himself to our teammate, and would only free himself to cause insidious mischief, which would invariably result in an explosion of hysterics, his eyes bursting with tears and his mouth, as wide as canyon, unleashing a sonorous wail when something went wrong. On the other hand, Alice remained in the distance, content to smile and shyly wave her hand at our team while hiding behind her sisters. And last but not least, of our precious goonies, Sunny undoubtedly was the photographer extraordinaire, always in charge of the school’s camera, snapping away liberally, never allowing any passing moment to escape his shot.
That I learned on this trip so much about my teammates verily surprised me, as I thought the relationships that we had established were already mature, not hiding any new bump, any sharp edge to surprise us from our friendly stupor. So, consider myself delightfully amazed at how a few slight changes in the personality mix can bring out the best, the most creative and the strangest in the group dynamic: admittedly, Candy and Tanya were the ideal foils for John, they eliciting the most humorous observations and reactions from my house church leader, they expertly constructing a depth of character that even last week, in the wake of the Guangdong biking trip, I never knew existed! Most of all, I’m glad to have been a part of such a harmonious fellowship, for the fact that we could prayer together as one, and encourage each other too, and all the more as we saw the day approaching.
Ox-drawn plough-seeder, 1637

Image by Marcel Douwe Dekker
Source: Song Yingxing (1637) Tiangong Kaiwu, part 1on agriculture, irrigation, and hydraulic China engineering
Image taken from page 429 of ‘China, historisch romantisch, malerisch. [A translation of parts of “China, in a series of views … By Thomas Allom Esq. with historical and descriptive notes by the Rev. G. N. Wright.” With a selection from the China engravings.]
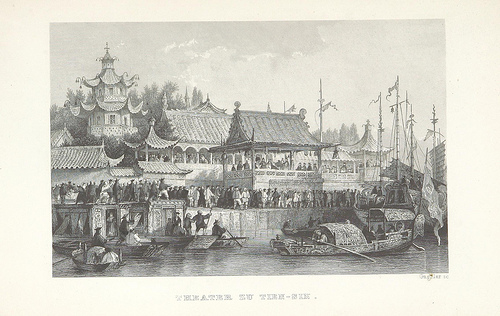
Image by The British Library
Image taken from:
Title: "China, historisch romantisch, malerisch. [A translation of parts of “China, in a series of views … By Thomas Allom Esq. with historical and descriptive notes by the Rev. G. N. Wright.” With a selection from the China engravings.]", "Appendix"
Contributor: ALLOM, Thomas.
Contributor: WRIGHT, George Newenham.
Author: China
Shelfmark: "British Library HMNTS 792.i.30."
Page: 429
Place of Publishing: Carlsruhe
Date of Publishing: 1843
Issuance: monographic
Identifier: 000687360
Note: The colours, contrast and appearance of these illustrations are unlikely to be true to life. They are derived from scanned images that have been enhanced for machine interpretation and have been altered from their originals.
If you wish to purchase a high quality copy of the page that this image is drawn from, please order it here. Please note that you will need to enter details from the above list – such as the shelfmark, the page, the book’s volume and so on – when filling out your order.
Explore:
Find this item in the British Library catalogue, ‘Explore’.
Open the page in the British Library’s itemViewer (page: 429)
Download the PDF for this book
Click here to see all the illustrations in this book and click here to browse other illustrations published in books in the same year. Please click on the tags shown on the right-hand side for other ways to browse the illustrations.

Nice Rapid Prototype China photos
Check out these rapid prototype china images:
Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center: P-40 Warhawk, SR-71 Blackbird, Naval Aircraft Factory N3N seaplane, Space Shuttle Enterprise

Image by Chris Devers
Quoting Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Curtiss P-40E Warhawk (Kittyhawk IA):
Whether known as the Warhawk, Tomahawk, or Kittyhawk, the Curtiss P-40 proved to be a successful, versatile fighter during the first half of World War II. The shark-mouthed Tomahawks that Gen. Claire Chennault’s "Flying Tigers" flew in China against the Japanese remain among the most popular airplanes of the war. P-40E pilot Lt. Boyd D. Wagner became the first American ace of World War II when he shot down six Japanese aircraft in the Philippines in mid-December 1941.
Curtiss-Wright built this airplane as Model 87-A3 and delivered it to Canada as a Kittyhawk I in 1941. It served until 1946 in No. 111 Squadron, Royal Canadian Air Force. U.S. Air Force personnel at Andrews Air Force Base restored it in 1975 to represent an aircraft of the 75th Fighter Squadron, 23rd Fighter Group, 14th Air Force.
Donated by the Exchange Club in Memory of Kellis Forbes.
Manufacturer:
Curtiss Aircraft Company
Date:
1939
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 330 x 970cm, 2686kg, 1140cm (10ft 9 15/16in. x 31ft 9 7/8in., 5921.6lb., 37ft 4 13/16in.)
Materials:
All-metal, semi-monocoque
Physical Description:
Single engine, single seat, fighter aircraft.
• • • • •
See more photos of this, and the Wikipedia article.
Details, quoting from Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird:
No reconnaissance aircraft in history has operated globally in more hostile airspace or with such complete impunity than the SR-71, the world’s fastest jet-propelled aircraft. The Blackbird’s performance and operational achievements placed it at the pinnacle of aviation technology developments during the Cold War.
This Blackbird accrued about 2,800 hours of flight time during 24 years of active service with the U.S. Air Force. On its last flight, March 6, 1990, Lt. Col. Ed Yielding and Lt. Col. Joseph Vida set a speed record by flying from Los Angeles to Washington, D.C., in 1 hour, 4 minutes, and 20 seconds, averaging 3,418 kilometers (2,124 miles) per hour. At the flight’s conclusion, they landed at Washington-Dulles International Airport and turned the airplane over to the Smithsonian.
Transferred from the United States Air Force.
Manufacturer:
Lockheed Aircraft Corporation
Designer:
Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson
Date:
1964
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 55ft 7in. x 107ft 5in., 169998.5lb. (5.638m x 16.942m x 32.741m, 77110.8kg)
Other: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 107ft 5in. x 55ft 7in. (5.638m x 32.741m x 16.942m)
Materials:
Titanium
Physical Description:
Twin-engine, two-seat, supersonic strategic reconnaissance aircraft; airframe constructed largley of titanium and its alloys; vertical tail fins are constructed of a composite (laminated plastic-type material) to reduce radar cross-section; Pratt and Whitney J58 (JT11D-20B) turbojet engines feature large inlet shock cones.
• • • • •
Quoting Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Naval Aircraft Factory N3N:
In 1934 the Naval Aircraft Factory in Philadelphia was tasked to manufacture a new primary trainer for the U.S. Navy. Following successful tests, this little biplane trainer was built in both land and seaplane versions. The Navy initially ordered 179 N3N-1 models, and the factory began producing more than 800 N3N-3 models in 1938. U.S. Navy primary flight training schools used N3Ns extensively throughout World War II. A few of the seaplane version were retained for primary training at the U.S. Naval Academy. In 1961 they became the last biplanes retired from U.S. military service.
This N3N-3 was transferred from Cherry Point to Annapolis in 1946, where it served as a seaplane trainer. It was restored and displayed at the Naval Academy Museum before being transferred here.
Transferred from the United States Navy
Manufacturer:
Naval Aircraft Factory
Date:
1941
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 10ft 9 15/16in. x 25ft 7 1/16in. x 34ft 1 7/16in., 2090lb. (330 x 780 x 1040cm, 948kg)
Materials:
bolted steel-tube fuselage construction with removable side panels wings, also constructed internally of all metal, covered with fabric like the fuselage and tail.
Physical Description:
Bright yellow bi-plane, hand crank start. Cockpit instrumentation consists of an altimeter, tachometer, airspeed indicator, compass, turn and bank indicator, and a combination fuel and oil temperature and pressure gauge, floats.
• • • • •
See more photos of this, and the Wikipedia article.
Details, quoting from Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Space Shuttle Enterprise:
Manufacturer:
Rockwell International Corporation
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 57 ft. tall x 122 ft. long x 78 ft. wing span, 150,000 lb.
(1737.36 x 3718.57 x 2377.44cm, 68039.6kg)
Materials:
Aluminum airframe and body with some fiberglass features; payload bay doors are graphite epoxy composite; thermal tiles are simulated (polyurethane foam) except for test samples of actual tiles and thermal blankets.
The first Space Shuttle orbiter, "Enterprise," is a full-scale test vehicle used for flights in the atmosphere and tests on the ground; it is not equipped for spaceflight. Although the airframe and flight control elements are like those of the Shuttles flown in space, this vehicle has no propulsion system and only simulated thermal tiles because these features were not needed for atmospheric and ground tests. "Enterprise" was rolled out at Rockwell International’s assembly facility in Palmdale, California, in 1976. In 1977, it entered service for a nine-month-long approach-and-landing test flight program. Thereafter it was used for vibration tests and fit checks at NASA centers, and it also appeared in the 1983 Paris Air Show and the 1984 World’s Fair in New Orleans. In 1985, NASA transferred "Enterprise" to the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum.
Transferred from National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center: SR-71 Blackbird (tail view)

Image by Chris Devers
See more photos of this, and the Wikipedia article.
Details, quoting from Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird:
No reconnaissance aircraft in history has operated globally in more hostile airspace or with such complete impunity than the SR-71, the world’s fastest jet-propelled aircraft. The Blackbird’s performance and operational achievements placed it at the pinnacle of aviation technology developments during the Cold War.
This Blackbird accrued about 2,800 hours of flight time during 24 years of active service with the U.S. Air Force. On its last flight, March 6, 1990, Lt. Col. Ed Yielding and Lt. Col. Joseph Vida set a speed record by flying from Los Angeles to Washington, D.C., in 1 hour, 4 minutes, and 20 seconds, averaging 3,418 kilometers (2,124 miles) per hour. At the flight’s conclusion, they landed at Washington-Dulles International Airport and turned the airplane over to the Smithsonian.
Transferred from the United States Air Force.
Manufacturer:
Lockheed Aircraft Corporation
Designer:
Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson
Date:
1964
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 55ft 7in. x 107ft 5in., 169998.5lb. (5.638m x 16.942m x 32.741m, 77110.8kg)
Other: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 107ft 5in. x 55ft 7in. (5.638m x 32.741m x 16.942m)
Materials:
Titanium
Physical Description:
Twin-engine, two-seat, supersonic strategic reconnaissance aircraft; airframe constructed largley of titanium and its alloys; vertical tail fins are constructed of a composite (laminated plastic-type material) to reduce radar cross-section; Pratt and Whitney J58 (JT11D-20B) turbojet engines feature large inlet shock cones.
Long Description:
No reconnaissance aircraft in history has operated in more hostile airspace or with such complete impunity than the SR-71 Blackbird. It is the fastest aircraft propelled by air-breathing engines. The Blackbird’s performance and operational achievements placed it at the pinnacle of aviation technology developments during the Cold War. The airplane was conceived when tensions with communist Eastern Europe reached levels approaching a full-blown crisis in the mid-1950s. U.S. military commanders desperately needed accurate assessments of Soviet worldwide military deployments, particularly near the Iron Curtain. Lockheed Aircraft Corporation’s subsonic U-2 (see NASM collection) reconnaissance aircraft was an able platform but the U. S. Air Force recognized that this relatively slow aircraft was already vulnerable to Soviet interceptors. They also understood that the rapid development of surface-to-air missile systems could put U-2 pilots at grave risk. The danger proved reality when a U-2 was shot down by a surface to air missile over the Soviet Union in 1960.
Lockheed’s first proposal for a new high speed, high altitude, reconnaissance aircraft, to be capable of avoiding interceptors and missiles, centered on a design propelled by liquid hydrogen. This proved to be impracticable because of considerable fuel consumption. Lockheed then reconfigured the design for conventional fuels. This was feasible and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), already flying the Lockheed U-2, issued a production contract for an aircraft designated the A-12. Lockheed’s clandestine ‘Skunk Works’ division (headed by the gifted design engineer Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson) designed the A-12 to cruise at Mach 3.2 and fly well above 18,288 m (60,000 feet). To meet these challenging requirements, Lockheed engineers overcame many daunting technical challenges. Flying more than three times the speed of sound generates 316° C (600° F) temperatures on external aircraft surfaces, which are enough to melt conventional aluminum airframes. The design team chose to make the jet’s external skin of titanium alloy to which shielded the internal aluminum airframe. Two conventional, but very powerful, afterburning turbine engines propelled this remarkable aircraft. These power plants had to operate across a huge speed envelope in flight, from a takeoff speed of 334 kph (207 mph) to more than 3,540 kph (2,200 mph). To prevent supersonic shock waves from moving inside the engine intake causing flameouts, Johnson’s team had to design a complex air intake and bypass system for the engines.
Skunk Works engineers also optimized the A-12 cross-section design to exhibit a low radar profile. Lockheed hoped to achieve this by carefully shaping the airframe to reflect as little transmitted radar energy (radio waves) as possible, and by application of special paint designed to absorb, rather than reflect, those waves. This treatment became one of the first applications of stealth technology, but it never completely met the design goals.
Test pilot Lou Schalk flew the single-seat A-12 on April 24, 1962, after he became airborne accidentally during high-speed taxi trials. The airplane showed great promise but it needed considerable technical refinement before the CIA could fly the first operational sortie on May 31, 1967 – a surveillance flight over North Vietnam. A-12s, flown by CIA pilots, operated as part of the Air Force’s 1129th Special Activities Squadron under the "Oxcart" program. While Lockheed continued to refine the A-12, the U. S. Air Force ordered an interceptor version of the aircraft designated the YF-12A. The Skunk Works, however, proposed a "specific mission" version configured to conduct post-nuclear strike reconnaissance. This system evolved into the USAF’s familiar SR-71.
Lockheed built fifteen A-12s, including a special two-seat trainer version. Two A-12s were modified to carry a special reconnaissance drone, designated D-21. The modified A-12s were redesignated M-21s. These were designed to take off with the D-21 drone, powered by a Marquart ramjet engine mounted on a pylon between the rudders. The M-21 then hauled the drone aloft and launched it at speeds high enough to ignite the drone’s ramjet motor. Lockheed also built three YF-12As but this type never went into production. Two of the YF-12As crashed during testing. Only one survives and is on display at the USAF Museum in Dayton, Ohio. The aft section of one of the "written off" YF-12As which was later used along with an SR-71A static test airframe to manufacture the sole SR-71C trainer. One SR-71 was lent to NASA and designated YF-12C. Including the SR-71C and two SR-71B pilot trainers, Lockheed constructed thirty-two Blackbirds. The first SR-71 flew on December 22, 1964. Because of extreme operational costs, military strategists decided that the more capable USAF SR-71s should replace the CIA’s A-12s. These were retired in 1968 after only one year of operational missions, mostly over southeast Asia. The Air Force’s 1st Strategic Reconnaissance Squadron (part of the 9th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing) took over the missions, flying the SR-71 beginning in the spring of 1968.
After the Air Force began to operate the SR-71, it acquired the official name Blackbird– for the special black paint that covered the airplane. This paint was formulated to absorb radar signals, to radiate some of the tremendous airframe heat generated by air friction, and to camouflage the aircraft against the dark sky at high altitudes.
Experience gained from the A-12 program convinced the Air Force that flying the SR-71 safely required two crew members, a pilot and a Reconnaissance Systems Officer (RSO). The RSO operated with the wide array of monitoring and defensive systems installed on the airplane. This equipment included a sophisticated Electronic Counter Measures (ECM) system that could jam most acquisition and targeting radar. In addition to an array of advanced, high-resolution cameras, the aircraft could also carry equipment designed to record the strength, frequency, and wavelength of signals emitted by communications and sensor devices such as radar. The SR-71 was designed to fly deep into hostile territory, avoiding interception with its tremendous speed and high altitude. It could operate safely at a maximum speed of Mach 3.3 at an altitude more than sixteen miles, or 25,908 m (85,000 ft), above the earth. The crew had to wear pressure suits similar to those worn by astronauts. These suits were required to protect the crew in the event of sudden cabin pressure loss while at operating altitudes.
To climb and cruise at supersonic speeds, the Blackbird’s Pratt & Whitney J-58 engines were designed to operate continuously in afterburner. While this would appear to dictate high fuel flows, the Blackbird actually achieved its best "gas mileage," in terms of air nautical miles per pound of fuel burned, during the Mach 3+ cruise. A typical Blackbird reconnaissance flight might require several aerial refueling operations from an airborne tanker. Each time the SR-71 refueled, the crew had to descend to the tanker’s altitude, usually about 6,000 m to 9,000 m (20,000 to 30,000 ft), and slow the airplane to subsonic speeds. As velocity decreased, so did frictional heat. This cooling effect caused the aircraft’s skin panels to shrink considerably, and those covering the fuel tanks contracted so much that fuel leaked, forming a distinctive vapor trail as the tanker topped off the Blackbird. As soon as the tanks were filled, the jet’s crew disconnected from the tanker, relit the afterburners, and again climbed to high altitude.
Air Force pilots flew the SR-71 from Kadena AB, Japan, throughout its operational career but other bases hosted Blackbird operations, too. The 9th SRW occasionally deployed from Beale AFB, California, to other locations to carryout operational missions. Cuban missions were flown directly from Beale. The SR-71 did not begin to operate in Europe until 1974, and then only temporarily. In 1982, when the U.S. Air Force based two aircraft at Royal Air Force Base Mildenhall to fly monitoring mission in Eastern Europe.
When the SR-71 became operational, orbiting reconnaissance satellites had already replaced manned aircraft to gather intelligence from sites deep within Soviet territory. Satellites could not cover every geopolitical hotspot so the Blackbird remained a vital tool for global intelligence gathering. On many occasions, pilots and RSOs flying the SR-71 provided information that proved vital in formulating successful U. S. foreign policy. Blackbird crews provided important intelligence about the 1973 Yom Kippur War, the Israeli invasion of Lebanon and its aftermath, and pre- and post-strike imagery of the 1986 raid conducted by American air forces on Libya. In 1987, Kadena-based SR-71 crews flew a number of missions over the Persian Gulf, revealing Iranian Silkworm missile batteries that threatened commercial shipping and American escort vessels.
As the performance of space-based surveillance systems grew, along with the effectiveness of ground-based air defense networks, the Air Force started to lose enthusiasm for the expensive program and the 9th SRW ceased SR-71 operations in January 1990. Despite protests by military leaders, Congress revived the program in 1995. Continued wrangling over operating budgets, however, soon led to final termination. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration retained two SR-71As and the one SR-71B for high-speed research projects and flew these airplanes until 1999.
On March 6, 1990, the service career of one Lockheed SR-71A Blackbird ended with a record-setting flight. This special airplane bore Air Force serial number 64-17972. Lt. Col. Ed Yeilding and his RSO, Lieutenant Colonel Joseph Vida, flew this aircraft from Los Angeles to Washington D.C. in 1 hour, 4 minutes, and 20 seconds, averaging a speed of 3,418 kph (2,124 mph). At the conclusion of the flight, ‘972 landed at Dulles International Airport and taxied into the custody of the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum. At that time, Lt. Col. Vida had logged 1,392.7 hours of flight time in Blackbirds, more than that of any other crewman.
This particular SR-71 was also flown by Tom Alison, a former National Air and Space Museum’s Chief of Collections Management. Flying with Detachment 1 at Kadena Air Force Base, Okinawa, Alison logged more than a dozen ‘972 operational sorties. The aircraft spent twenty-four years in active Air Force service and accrued a total of 2,801.1 hours of flight time.
Wingspan: 55’7"
Length: 107’5"
Height: 18’6"
Weight: 170,000 Lbs
Reference and Further Reading:
Crickmore, Paul F. Lockheed SR-71: The Secret Missions Exposed. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 1996.
Francillon, Rene J. Lockheed Aircraft Since 1913. Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press, 1987.
Johnson, Clarence L. Kelly: More Than My Share of It All. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1985.
Miller, Jay. Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works. Leicester, U.K.: Midland Counties Publishing Ltd., 1995.
Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird curatorial file, Aeronautics Division, National Air and Space Museum.
DAD, 11-11-01
Pump up the 3d printer
Image by · · · — — — · · ·
MakerBot with ABS? feed.
Lastest China Milling And China Machining auctions
milling and machining eBay auctions you should keep an eye on:
[wprebay kw=”milling+and+machining” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”milling+and+machining” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”milling+and+machining” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]
Most popular Aluminum China Machining auctions
Aluminum China Machining on eBay:
[wprebay kw=”aluminum+machining” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”aluminum+machining” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
Lastest Custom China Machining Services auctions
Most popular custom China machining services eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”custom+machining+services” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”custom+machining+services” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
Lastest Aluminum China Machined Parts News
parts

Image by Inha Leex Hale
Most popular Precision China Manufacturing auctions
precision China manufacturing eBay auctions you should keep an eye on:
[wprebay kw=”precision+manufacturing” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”precision+manufacturing” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”precision+manufacturing” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]
Most popular Cnc Rapid China Prototyping auctions
Most popular cnc China rapid prototyping eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”cnc+rapid+prototyping” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”cnc+rapid+prototyping” num=”3″ ebcat=”-1″]
Esterline – 5-axis Aerospace China Machining on a Mori Seiki NT
Esterline & Sons explains how the combination of PowerMILL and PartMaker help them perform 5-axis simultaneous machining of aerospace parts on their Mori NT …
Video Rating: 0 / 5