Most popular cnc machining prototyping eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”cnc+machining+prototyping” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”cnc+machining+prototyping” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”cnc+machining+prototyping” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]
Aluminium Machining China
Most popular cnc machining prototyping eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”cnc+machining+prototyping” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”cnc+machining+prototyping” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”cnc+machining+prototyping” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]
Most popular rapid prototype machining eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”rapid+prototype+machining” num=”3″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+prototype+machining” num=”4″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+prototype+machining” num=”5″ ebcat=”-1″]
rapid prototype China machining eBay auctions you should keep an eye on:
[wprebay kw=”rapid+prototype+machining” num=”3″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+prototype+machining” num=”4″ ebcat=”-1″]
Most popular cnc rapid prototype eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”cnc+rapid+prototype” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”cnc+rapid+prototype” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
Most popular rapid cnc prototyping eBay auctions:
[wprebay kw=”rapid+cnc+prototyping” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+cnc+prototyping” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+cnc+prototyping” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]
rapid cnc China machining eBay auctions you should keep an eye on:
[wprebay kw=”rapid+cnc+machining” num=”0″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+cnc+machining” num=”1″ ebcat=”-1″]
[wprebay kw=”rapid+cnc+machining” num=”2″ ebcat=”-1″]

Check out these rapid cnc prototyping images:
3D Printers

Image by Cory M. Grenier
ITU Rapid China Prototyping Workshop
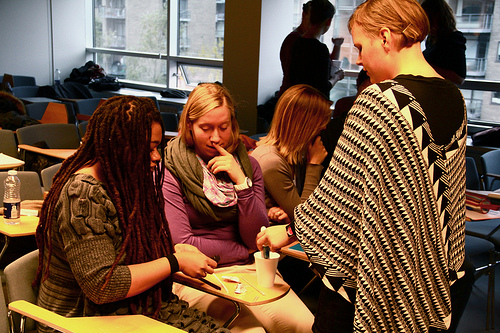
Image by geekphysical
A China rapid prototyping workshop for Master of Interaction Design students at ITU. An introduction to China rapid prototyping as a concept and as a practice, both in the quick and dirty sense (using available materials to achieve proof of concept) and through awareness of tools available such as the China CNC machine, the Rep Rap machine, and use and knowledge of materials, processes and communities. Part lecture, part hands-on prototyping complete with proof of concept from each group.

Some cool rapid China machining services images:
Rapid fire guns before Tchataldja #1 (LOC)

Image by The Library of Congress
Bain News Service,, publisher.
Rapid fire guns before Tchataldja #1
[between ca. 1910 and ca. 1915]
1 negative : glass ; 5 x 7 in. or smaller.
Notes:
Title from data provided by the Bain News Service on the negative.
Photograph shows Bulgarians? with guns near Çatalca, Turkey during the Balkan Wars. (Source: Flickr Commons project, 2009)
Forms part of: George Grantham Bain Collection (Library of Congress).
Format: Glass negatives.
Rights Info: No known restrictions on publication.
Repository: Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA, hdl.loc.gov/loc.pnp/pp.print
General information about the Bain Collection is available at hdl.loc.gov/loc.pnp/pp.ggbain
Higher resolution image is available (Persistent URL): hdl.loc.gov/loc.pnp/ggbain.11701
Call Number: LC-B2- 2532-15
Staff Sgt. Salvatore A. Giunta
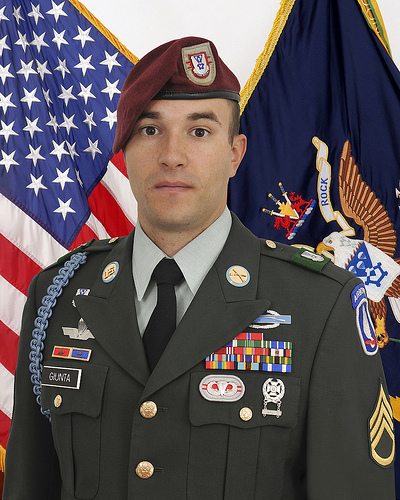

Image by US Army Africa
Staff Sgt. Salvatore A. Giunta
U.S. Army photo
President Barack Obama presented the Medal of Honor for conspicuous gallantry to Staff Sgt. Salvatore Giunta, U.S. Army, in a ceremony held in the East Room of the White House Nov. 16, 2010 — the first living service member from the Iraq or Afghanistan wars to receive it.
When enemy forces in Afghanistan’s Korengal Valley ambushed then-Spc. Giunta’s platoon on the evening of Oct. 25, 2007, the infantry team leader braved heavy enemy fire to rescue fellow paratroopers.
(To veiw the 30-minute U.S. Army Africa video interveiw with Staff Sgt. Giunta, go to: Vicenza paratrooper to be awarded Medal of Honor from US Army Africa on Vimeo.
Giunta, of Company B, 2nd Battalion, 503rd Infantry Regiment, 173rd Airborne Brigade Combat Team, will be awarded the Medal of Honor, the U.S. military’s highest award for valor under fire.
The Hiawatha, Iowa-native is the first living service member to earn the award since Vietnam. The medal will be presented in a ceremony at a date and time still to be determined.
A 2003 graduate of Cedar Rapids Kennedy High School, Giunta has served two tours of Afghanistan. Now a staff sergeant serving in Vicenza, Italy, Giunta of Hiawatha, Iowa, knew of the nomination several months ago, but the announcement still came as a shock.
“This is a great honor, but it is not mine to take sole ownership of. I only did the next thing that needed to be done, and I was only able to do that because all of the men around me had the rest taken care of. It’s hard to take credit for simply taking the next step when so many steps had already been taken by everyone else,” Giunta said.
Not a day goes by that Giunta, now a staff sergeant serving at Vicenza’s Caserma Ederle, does not recall what he and fellow paratroopers faced that evening.
The first platoon of Company B – known to 173rd paratroopers as “Battle Company” – were heading back to their base camp in Afghanistan’s Korengal Valley following a long day watching over fellow paratroopers in an Afghan village. It was the final day of Operation Rock Avalanche. Throughout the day, enemy radio intercepts spoke of an impending attack.
Evening was approaching as Giunta’s platoon stretched in to a snaking file down the spur to the Korengal outpost. Roughly thirty paces separated each paratrooper as the moved out.
Sgt. Joshua Brennan, a 22-year-old team leader from Ontario, Ore., on his second tour in Afghanistan, was up front. Behind Brennan, manning an M249 squad automatic weapon, was Spc. Frank Eckrode then squad leader, Staff Sgt. Erick Gallardo, 24, Chula Vista, Calif.
AH-64 Apache helicopters chopped the moonlit evening above as the platoon made their way down goat trails.
Giunta, who carried an M-4 assault rifle was just behind with his team. Pfc. Kaleb Casey carried his M249 squad automatic weapon, followed by Pfc. Garrett Clary with an M203, a 5.56 mm rifle combined with a 40 millimeter grenade launcher.
Along their path, more than a dozen enemy fighters waited, readying their Russian-style rocket propelled grenades, PKM 7.62 mm heavy machine guns, and Kalishnikov rifles. They had set up an L-shape, with an RPG and PKM at the apex of the formation. As Brennan walked just 30 feet from their over watch position, the enemy open fired.
An enemy RPG exploded, followed by a burst of machine gun fire. Brennan fell to the ground. China Machine guns fired at the platoon’s flank. Eckrode was hit. He dropped to the ground, returned fire and tried to find cover.
Gallardo tried to run forward, but was met with RPG explosions and sustained machine gun fire. He returned fire and started back to Giunta’s position, falling into a ditch as an AK-47 round struck his helmet. Giunta jumped up, exposing himself to deadly fire, to assist his squad leader.
Giunta ran just a few steps when two enemy AK-47 rounds struck his body. The first shot hit the body armor on Giunta’s chest, the second hit over his left shoulder, striking a disposable rocket launcher strapped to his rucksack. But Giunta kept going, reaching Gallardo and dragging him back to where Giunta’s fire team had begun fighting back.
Gallardo got Giunta’s team online and the four paratroopers began bounding through withering enemy fire to rescue Eckrode and Brennan. Dropping for cover, they prepared fragmentation grenades to throw at the enemy to cover their next move. Casey continued to fire his machine gun at enemy muzzle flashes, less than a half city block away. Gallardo counted to three and the team hurled grenades toward enemy positions. Once they heard the explosions, they moved closer to their wounded comrades.
Eckrode called out. He was wounded, but still trying to fight. Gallardo started first aid on Eckrode while Casey, who found a bullet hole in his uniform, scanned for enemy targets.
Giunta and Clary kept running toward where Brennan fell, only to find two enemy fighters carrying a severely-wounded Brennan away. While still running, Giunta fired his assault rifle, causing them to drop Brennan and flee. Giunta emptied the rest of his magazine, killing one enemy. Giunta knelt down to help Brennan as Clary ran past, firing 40-milimeter rounds toward the retreating enemy.
Giunta saw Brennan’s injuries were severe and required more than he could offer there on the battlefield. He removed Brennan’s gear and began treating his buddy, while calling back to Gallardo for help. Brennan was trying to talk. Giunta reassured his friend as he tended to Brennan’s wounds.
Other paratroopers from the platoon were also wounded. Spc. Hugo Mendoza, was killed. Brennan, who was hoisted into a helicopter, later succumbed to his wounds.
“Giunta is a great friend and an outstanding paratrooper,” said Gallardo, now serving with Battle Company in Afghanistan. “His actions that day meant the difference between life and death to myself and other Soldiers. For that I am grateful.”
To learn more about U.S. Army Africa visit our official website at www.usaraf.army.mil
Official Twitter Feed: www.twitter.com/usarmyafrica
Official Vimeo video channel: www.vimeo.com/usarmyafrica

Visit.www.datron.com. DATRON CNC China Milling China China Machines are high-speed machining centers designed for efficiency with small micro tools. Capable of milling, drilli…
Video Rating: 0 / 5

My Website http://machineworkshop.com/ Help Support CncShopMill http://goo.gl/GRG0RG This video shows how easy is is to make a prototype part when your mill …

Check out these rapid prototype china images:
Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center: P-40 Warhawk, SR-71 Blackbird, Naval Aircraft Factory N3N seaplane, Space Shuttle Enterprise

Image by Chris Devers
Quoting Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Curtiss P-40E Warhawk (Kittyhawk IA):
Whether known as the Warhawk, Tomahawk, or Kittyhawk, the Curtiss P-40 proved to be a successful, versatile fighter during the first half of World War II. The shark-mouthed Tomahawks that Gen. Claire Chennault’s "Flying Tigers" flew in China against the Japanese remain among the most popular airplanes of the war. P-40E pilot Lt. Boyd D. Wagner became the first American ace of World War II when he shot down six Japanese aircraft in the Philippines in mid-December 1941.
Curtiss-Wright built this airplane as Model 87-A3 and delivered it to Canada as a Kittyhawk I in 1941. It served until 1946 in No. 111 Squadron, Royal Canadian Air Force. U.S. Air Force personnel at Andrews Air Force Base restored it in 1975 to represent an aircraft of the 75th Fighter Squadron, 23rd Fighter Group, 14th Air Force.
Donated by the Exchange Club in Memory of Kellis Forbes.
Manufacturer:
Curtiss Aircraft Company
Date:
1939
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 330 x 970cm, 2686kg, 1140cm (10ft 9 15/16in. x 31ft 9 7/8in., 5921.6lb., 37ft 4 13/16in.)
Materials:
All-metal, semi-monocoque
Physical Description:
Single engine, single seat, fighter aircraft.
• • • • •
See more photos of this, and the Wikipedia article.
Details, quoting from Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird:
No reconnaissance aircraft in history has operated globally in more hostile airspace or with such complete impunity than the SR-71, the world’s fastest jet-propelled aircraft. The Blackbird’s performance and operational achievements placed it at the pinnacle of aviation technology developments during the Cold War.
This Blackbird accrued about 2,800 hours of flight time during 24 years of active service with the U.S. Air Force. On its last flight, March 6, 1990, Lt. Col. Ed Yielding and Lt. Col. Joseph Vida set a speed record by flying from Los Angeles to Washington, D.C., in 1 hour, 4 minutes, and 20 seconds, averaging 3,418 kilometers (2,124 miles) per hour. At the flight’s conclusion, they landed at Washington-Dulles International Airport and turned the airplane over to the Smithsonian.
Transferred from the United States Air Force.
Manufacturer:
Lockheed Aircraft Corporation
Designer:
Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson
Date:
1964
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 55ft 7in. x 107ft 5in., 169998.5lb. (5.638m x 16.942m x 32.741m, 77110.8kg)
Other: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 107ft 5in. x 55ft 7in. (5.638m x 32.741m x 16.942m)
Materials:
Titanium
Physical Description:
Twin-engine, two-seat, supersonic strategic reconnaissance aircraft; airframe constructed largley of titanium and its alloys; vertical tail fins are constructed of a composite (laminated plastic-type material) to reduce radar cross-section; Pratt and Whitney J58 (JT11D-20B) turbojet engines feature large inlet shock cones.
• • • • •
Quoting Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Naval Aircraft Factory N3N:
In 1934 the Naval Aircraft Factory in Philadelphia was tasked to manufacture a new primary trainer for the U.S. Navy. Following successful tests, this little biplane trainer was built in both land and seaplane versions. The Navy initially ordered 179 N3N-1 models, and the factory began producing more than 800 N3N-3 models in 1938. U.S. Navy primary flight training schools used N3Ns extensively throughout World War II. A few of the seaplane version were retained for primary training at the U.S. Naval Academy. In 1961 they became the last biplanes retired from U.S. military service.
This N3N-3 was transferred from Cherry Point to Annapolis in 1946, where it served as a seaplane trainer. It was restored and displayed at the Naval Academy Museum before being transferred here.
Transferred from the United States Navy
Manufacturer:
Naval Aircraft Factory
Date:
1941
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 10ft 9 15/16in. x 25ft 7 1/16in. x 34ft 1 7/16in., 2090lb. (330 x 780 x 1040cm, 948kg)
Materials:
bolted steel-tube fuselage construction with removable side panels wings, also constructed internally of all metal, covered with fabric like the fuselage and tail.
Physical Description:
Bright yellow bi-plane, hand crank start. Cockpit instrumentation consists of an altimeter, tachometer, airspeed indicator, compass, turn and bank indicator, and a combination fuel and oil temperature and pressure gauge, floats.
• • • • •
See more photos of this, and the Wikipedia article.
Details, quoting from Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Space Shuttle Enterprise:
Manufacturer:
Rockwell International Corporation
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 57 ft. tall x 122 ft. long x 78 ft. wing span, 150,000 lb.
(1737.36 x 3718.57 x 2377.44cm, 68039.6kg)
Materials:
Aluminum airframe and body with some fiberglass features; payload bay doors are graphite epoxy composite; thermal tiles are simulated (polyurethane foam) except for test samples of actual tiles and thermal blankets.
The first Space Shuttle orbiter, "Enterprise," is a full-scale test vehicle used for flights in the atmosphere and tests on the ground; it is not equipped for spaceflight. Although the airframe and flight control elements are like those of the Shuttles flown in space, this vehicle has no propulsion system and only simulated thermal tiles because these features were not needed for atmospheric and ground tests. "Enterprise" was rolled out at Rockwell International’s assembly facility in Palmdale, California, in 1976. In 1977, it entered service for a nine-month-long approach-and-landing test flight program. Thereafter it was used for vibration tests and fit checks at NASA centers, and it also appeared in the 1983 Paris Air Show and the 1984 World’s Fair in New Orleans. In 1985, NASA transferred "Enterprise" to the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum.
Transferred from National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center: SR-71 Blackbird (tail view)

Image by Chris Devers
See more photos of this, and the Wikipedia article.
Details, quoting from Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum | Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird:
No reconnaissance aircraft in history has operated globally in more hostile airspace or with such complete impunity than the SR-71, the world’s fastest jet-propelled aircraft. The Blackbird’s performance and operational achievements placed it at the pinnacle of aviation technology developments during the Cold War.
This Blackbird accrued about 2,800 hours of flight time during 24 years of active service with the U.S. Air Force. On its last flight, March 6, 1990, Lt. Col. Ed Yielding and Lt. Col. Joseph Vida set a speed record by flying from Los Angeles to Washington, D.C., in 1 hour, 4 minutes, and 20 seconds, averaging 3,418 kilometers (2,124 miles) per hour. At the flight’s conclusion, they landed at Washington-Dulles International Airport and turned the airplane over to the Smithsonian.
Transferred from the United States Air Force.
Manufacturer:
Lockheed Aircraft Corporation
Designer:
Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson
Date:
1964
Country of Origin:
United States of America
Dimensions:
Overall: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 55ft 7in. x 107ft 5in., 169998.5lb. (5.638m x 16.942m x 32.741m, 77110.8kg)
Other: 18ft 5 15/16in. x 107ft 5in. x 55ft 7in. (5.638m x 32.741m x 16.942m)
Materials:
Titanium
Physical Description:
Twin-engine, two-seat, supersonic strategic reconnaissance aircraft; airframe constructed largley of titanium and its alloys; vertical tail fins are constructed of a composite (laminated plastic-type material) to reduce radar cross-section; Pratt and Whitney J58 (JT11D-20B) turbojet engines feature large inlet shock cones.
Long Description:
No reconnaissance aircraft in history has operated in more hostile airspace or with such complete impunity than the SR-71 Blackbird. It is the fastest aircraft propelled by air-breathing engines. The Blackbird’s performance and operational achievements placed it at the pinnacle of aviation technology developments during the Cold War. The airplane was conceived when tensions with communist Eastern Europe reached levels approaching a full-blown crisis in the mid-1950s. U.S. military commanders desperately needed accurate assessments of Soviet worldwide military deployments, particularly near the Iron Curtain. Lockheed Aircraft Corporation’s subsonic U-2 (see NASM collection) reconnaissance aircraft was an able platform but the U. S. Air Force recognized that this relatively slow aircraft was already vulnerable to Soviet interceptors. They also understood that the rapid development of surface-to-air missile systems could put U-2 pilots at grave risk. The danger proved reality when a U-2 was shot down by a surface to air missile over the Soviet Union in 1960.
Lockheed’s first proposal for a new high speed, high altitude, reconnaissance aircraft, to be capable of avoiding interceptors and missiles, centered on a design propelled by liquid hydrogen. This proved to be impracticable because of considerable fuel consumption. Lockheed then reconfigured the design for conventional fuels. This was feasible and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), already flying the Lockheed U-2, issued a production contract for an aircraft designated the A-12. Lockheed’s clandestine ‘Skunk Works’ division (headed by the gifted design engineer Clarence L. "Kelly" Johnson) designed the A-12 to cruise at Mach 3.2 and fly well above 18,288 m (60,000 feet). To meet these challenging requirements, Lockheed engineers overcame many daunting technical challenges. Flying more than three times the speed of sound generates 316° C (600° F) temperatures on external aircraft surfaces, which are enough to melt conventional aluminum airframes. The design team chose to make the jet’s external skin of titanium alloy to which shielded the internal aluminum airframe. Two conventional, but very powerful, afterburning turbine engines propelled this remarkable aircraft. These power plants had to operate across a huge speed envelope in flight, from a takeoff speed of 334 kph (207 mph) to more than 3,540 kph (2,200 mph). To prevent supersonic shock waves from moving inside the engine intake causing flameouts, Johnson’s team had to design a complex air intake and bypass system for the engines.
Skunk Works engineers also optimized the A-12 cross-section design to exhibit a low radar profile. Lockheed hoped to achieve this by carefully shaping the airframe to reflect as little transmitted radar energy (radio waves) as possible, and by application of special paint designed to absorb, rather than reflect, those waves. This treatment became one of the first applications of stealth technology, but it never completely met the design goals.
Test pilot Lou Schalk flew the single-seat A-12 on April 24, 1962, after he became airborne accidentally during high-speed taxi trials. The airplane showed great promise but it needed considerable technical refinement before the CIA could fly the first operational sortie on May 31, 1967 – a surveillance flight over North Vietnam. A-12s, flown by CIA pilots, operated as part of the Air Force’s 1129th Special Activities Squadron under the "Oxcart" program. While Lockheed continued to refine the A-12, the U. S. Air Force ordered an interceptor version of the aircraft designated the YF-12A. The Skunk Works, however, proposed a "specific mission" version configured to conduct post-nuclear strike reconnaissance. This system evolved into the USAF’s familiar SR-71.
Lockheed built fifteen A-12s, including a special two-seat trainer version. Two A-12s were modified to carry a special reconnaissance drone, designated D-21. The modified A-12s were redesignated M-21s. These were designed to take off with the D-21 drone, powered by a Marquart ramjet engine mounted on a pylon between the rudders. The M-21 then hauled the drone aloft and launched it at speeds high enough to ignite the drone’s ramjet motor. Lockheed also built three YF-12As but this type never went into production. Two of the YF-12As crashed during testing. Only one survives and is on display at the USAF Museum in Dayton, Ohio. The aft section of one of the "written off" YF-12As which was later used along with an SR-71A static test airframe to manufacture the sole SR-71C trainer. One SR-71 was lent to NASA and designated YF-12C. Including the SR-71C and two SR-71B pilot trainers, Lockheed constructed thirty-two Blackbirds. The first SR-71 flew on December 22, 1964. Because of extreme operational costs, military strategists decided that the more capable USAF SR-71s should replace the CIA’s A-12s. These were retired in 1968 after only one year of operational missions, mostly over southeast Asia. The Air Force’s 1st Strategic Reconnaissance Squadron (part of the 9th Strategic Reconnaissance Wing) took over the missions, flying the SR-71 beginning in the spring of 1968.
After the Air Force began to operate the SR-71, it acquired the official name Blackbird– for the special black paint that covered the airplane. This paint was formulated to absorb radar signals, to radiate some of the tremendous airframe heat generated by air friction, and to camouflage the aircraft against the dark sky at high altitudes.
Experience gained from the A-12 program convinced the Air Force that flying the SR-71 safely required two crew members, a pilot and a Reconnaissance Systems Officer (RSO). The RSO operated with the wide array of monitoring and defensive systems installed on the airplane. This equipment included a sophisticated Electronic Counter Measures (ECM) system that could jam most acquisition and targeting radar. In addition to an array of advanced, high-resolution cameras, the aircraft could also carry equipment designed to record the strength, frequency, and wavelength of signals emitted by communications and sensor devices such as radar. The SR-71 was designed to fly deep into hostile territory, avoiding interception with its tremendous speed and high altitude. It could operate safely at a maximum speed of Mach 3.3 at an altitude more than sixteen miles, or 25,908 m (85,000 ft), above the earth. The crew had to wear pressure suits similar to those worn by astronauts. These suits were required to protect the crew in the event of sudden cabin pressure loss while at operating altitudes.
To climb and cruise at supersonic speeds, the Blackbird’s Pratt & Whitney J-58 engines were designed to operate continuously in afterburner. While this would appear to dictate high fuel flows, the Blackbird actually achieved its best "gas mileage," in terms of air nautical miles per pound of fuel burned, during the Mach 3+ cruise. A typical Blackbird reconnaissance flight might require several aerial refueling operations from an airborne tanker. Each time the SR-71 refueled, the crew had to descend to the tanker’s altitude, usually about 6,000 m to 9,000 m (20,000 to 30,000 ft), and slow the airplane to subsonic speeds. As velocity decreased, so did frictional heat. This cooling effect caused the aircraft’s skin panels to shrink considerably, and those covering the fuel tanks contracted so much that fuel leaked, forming a distinctive vapor trail as the tanker topped off the Blackbird. As soon as the tanks were filled, the jet’s crew disconnected from the tanker, relit the afterburners, and again climbed to high altitude.
Air Force pilots flew the SR-71 from Kadena AB, Japan, throughout its operational career but other bases hosted Blackbird operations, too. The 9th SRW occasionally deployed from Beale AFB, California, to other locations to carryout operational missions. Cuban missions were flown directly from Beale. The SR-71 did not begin to operate in Europe until 1974, and then only temporarily. In 1982, when the U.S. Air Force based two aircraft at Royal Air Force Base Mildenhall to fly monitoring mission in Eastern Europe.
When the SR-71 became operational, orbiting reconnaissance satellites had already replaced manned aircraft to gather intelligence from sites deep within Soviet territory. Satellites could not cover every geopolitical hotspot so the Blackbird remained a vital tool for global intelligence gathering. On many occasions, pilots and RSOs flying the SR-71 provided information that proved vital in formulating successful U. S. foreign policy. Blackbird crews provided important intelligence about the 1973 Yom Kippur War, the Israeli invasion of Lebanon and its aftermath, and pre- and post-strike imagery of the 1986 raid conducted by American air forces on Libya. In 1987, Kadena-based SR-71 crews flew a number of missions over the Persian Gulf, revealing Iranian Silkworm missile batteries that threatened commercial shipping and American escort vessels.
As the performance of space-based surveillance systems grew, along with the effectiveness of ground-based air defense networks, the Air Force started to lose enthusiasm for the expensive program and the 9th SRW ceased SR-71 operations in January 1990. Despite protests by military leaders, Congress revived the program in 1995. Continued wrangling over operating budgets, however, soon led to final termination. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration retained two SR-71As and the one SR-71B for high-speed research projects and flew these airplanes until 1999.
On March 6, 1990, the service career of one Lockheed SR-71A Blackbird ended with a record-setting flight. This special airplane bore Air Force serial number 64-17972. Lt. Col. Ed Yeilding and his RSO, Lieutenant Colonel Joseph Vida, flew this aircraft from Los Angeles to Washington D.C. in 1 hour, 4 minutes, and 20 seconds, averaging a speed of 3,418 kph (2,124 mph). At the conclusion of the flight, ‘972 landed at Dulles International Airport and taxied into the custody of the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum. At that time, Lt. Col. Vida had logged 1,392.7 hours of flight time in Blackbirds, more than that of any other crewman.
This particular SR-71 was also flown by Tom Alison, a former National Air and Space Museum’s Chief of Collections Management. Flying with Detachment 1 at Kadena Air Force Base, Okinawa, Alison logged more than a dozen ‘972 operational sorties. The aircraft spent twenty-four years in active Air Force service and accrued a total of 2,801.1 hours of flight time.
Wingspan: 55’7"
Length: 107’5"
Height: 18’6"
Weight: 170,000 Lbs
Reference and Further Reading:
Crickmore, Paul F. Lockheed SR-71: The Secret Missions Exposed. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 1996.
Francillon, Rene J. Lockheed Aircraft Since 1913. Annapolis, Md.: Naval Institute Press, 1987.
Johnson, Clarence L. Kelly: More Than My Share of It All. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1985.
Miller, Jay. Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works. Leicester, U.K.: Midland Counties Publishing Ltd., 1995.
Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird curatorial file, Aeronautics Division, National Air and Space Museum.
DAD, 11-11-01
Pump up the 3d printer
Image by · · · — — — · · ·
MakerBot with ABS? feed.